
Accounting software, office suites, groupware, human resource management (HRM) systems, outsourcing relationship management, customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), business intelligence (BI) and analytics, business process management (BPM), and security software are just a few of the many applications that fall under the umbrella of "enterprise software.”
Enterprise applications promote collaboration and task coordination throughout the organization. The goal is to unify key corporate operations, e.g., sales & distribution, accounting, finance, human resources, inventory, and manufacturing, etc. The ideal enterprise system would have a single software architecture on a client/server platform that could govern all significant business operations in real time. The reach of corporate software is growing to connect businesses with clients, partners, and suppliers. Teams must make sure that all of the moving elements of an enterprise solution oscillate at the same frequency. Any discrepancy might result in data loss or application breakdown.
Organizations can only conduct thorough and dependable enterprise software testing through automation. It sure assists teams in performing thorough regression for enterprise-wide features, which can be cumbersome when driven manually.
Ready to Get Started?
Let our team experts walk you through how ACCELQ can assist you in achieving a true continuous testing automation
Characteristics of Enterprise solutions
Automating enterprise solutions is a challenge in itself. The “right” test automation strategy facilitates continuous quality improvement and supports new product development and the extension of existing product coverage. Before moving ahead to look at the challenges in an automation strategy, let us have a quick look at the characteristics of understanding enterprise solutions.
- 1. Enterprise applications are rich in business features
- 2. Working model – Scaled agile team structure
- 3. Deals with Persistent & Huge data volumes
- 4. Integration with other enterprise solutions
- 5. Cross DB and UI support (interoperability)
- 6. Complex UX
- 7. Maintaining and managing the performance of the growing application is a challenge.
- 8. Legacy solutions
- 9. Highly domain driven
Test Automation in the late 90s
The key to a stable automation strategy is to understand and work around the challenges in the ecosystem and application as a whole. Let us look at different application hosting models to identify the challenge in each one of the models.
On-Premise solutions
On-premise apps are internal solutions; The program resides in one or more computers and storage devices inside the company's facilities. These were the solutions developed more than a decade ago; present application designs do not follow this principle anymore. Several businesses continue to operate utilizing on-premise enterprise solutions. Organizations are forced to have a maintenance strategy as long as there are profitable consumers using these solutions. In these situations, it is not the best course of action to devote all of your time manually testing applications.
Challenges in on-premise testing
- 1. Setting up test environments
- 2. Upgrades and migration activities should be supported at a stretch
- 3. Clients continue to work on lower releases (reproducing the issues becomes a challenge)
- 4. The difference in production and test environments
- 5. On-premise applications are Monolith code, and user E2E scenarios can run long.
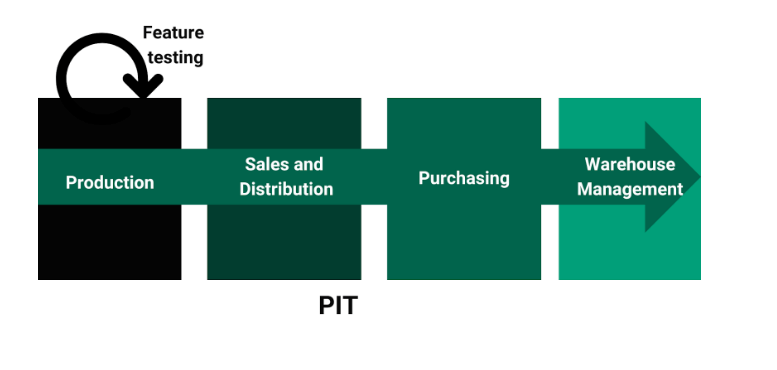
The best maintenance strategy would be to take the “feature testing” approach. Where each individual modules are tested in isolation, and integration scenarios are covered as part of “Process integration tests” (commonly known as PIT tests). These PIT tests need not be triggered on each CI build, they are best suited for Nightly runs.
PIT tests are very fragile; even if one module does not respond whole test suite may go for a toss.
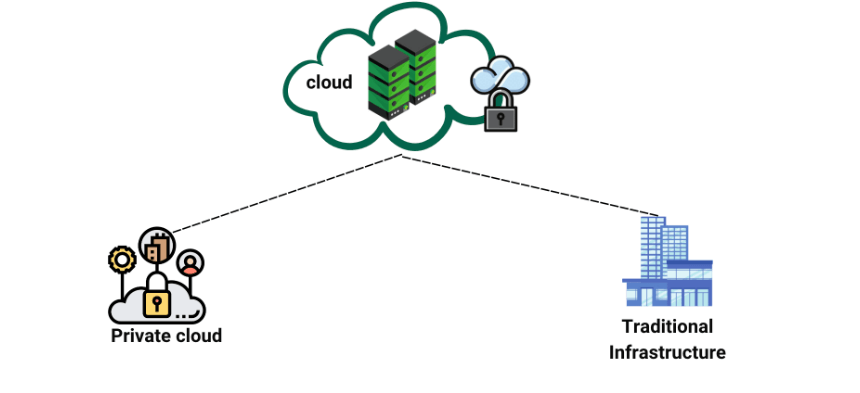
Hybrid cloud
Let's first define "Hybrid cloud" before talking about the difficulties with test automation in this configuration. The term "hybrid cloud" simply refers to a combination of on-premise (private cloud) and on-cloud (public cloud). The on-cloud component of a hybrid setup is used to host applications which demands less security but is also high-volume in nature, e.g., web-based emails. The on-premise segment was used to save more sensitive data and mission-critical activities.
In order to improve scalability and availability, existing legacy applications are being migrated to the cloud by many big companies as part of their enormous digital transformation. But this setup comes with its own challenges.
- 1. Hybrid technology
- 2. Split automation status
- 3. Keeping up with all the upgrades
- 4. Hot fixes or enhancement testing takes a longer time.
- 5. Need to learn multiple technologies involved
- 6. Interoperability between different versions of UI and DB
The bulk of existing automation systems only supports web-based apps. As a result, it is difficult for test teams to decide on a single automation framework. Teams are compelled to build bespoke methods in order to collaborate on two separate test frameworks. It's like adding to an already problematic situation. Low-code/No-Code solutions like ACCELQ are the best chance for overcoming this difficulty. In such cases, they support teams in achieving unified automation across tech stacks like web, API, mobile, database, desktop, and packaged apps.
Cloud solutions
Clouds offer enterprises a way to access applications and services without investing in infrastructure, promoting faster delivery cycles. Cloud computing also offers a set of different challenges that enterprises need to overcome, such as testing their applications. With cloud, the scalability testing will no longer be a challenge due to the autoscaling facility. Virtual users can be simulated at any point in time to inject artificial load onto the application.
With cloud hosting, tight coupling on location is eliminated. The application can be accessed from anywhere at any point in time. Now, most of the test service offerings are cloud-hosted, which makes testing framework integration much easier than before.
The test environments can be spun up anytime with any configuration of choice, it is just a button click away. Any number of test environments can be set up and teared down at a very low cost, unlike on-premise infrastructure. This gives a unique opportunity for the test automation script to start the test from a clean state of the application. This also eliminates stale data or the fear of test data being tampered by other users. Cloud solutions are great for collaboration; multiple team members can contribute in parallel.
Challenges in cloud applications are
- 1. Ramp up time
- 2. Security
- 3. Service availability
- 4. Tightly coupled services
- 5. Technical architecture understanding is a must
Cross-integrations with External solutions
In Enterprise applications, everything was built in-house. Development teams were guided to develop required functionalities within the ecosystem. Businesses soon realized not everything could be done internally as it would be cost and time inefficient. This also reduces the amount of time available for innovation development. To co-create the ecosystem, several firms began to utilize each other's solutions. As part of the user journey, current corporate solutions interface with external third-party apps.
This presents a unique difficulty for test automation,
- 1. Beginning with “Cross-origin Resource sharing,” in which scripts fail when relocated to a different domain.
- 2. The next difference in UI Technology and implementations is that the test team may have selected the automation framework compatible with their tech stack. However, supporting third-party applications may become tedious.
- 3. Support in the event of third-party program failures or problems. The entire integration tests run is halted until the problem in the external solution is rectified.
In all the above scenarios, testing teams are in a constant challenge to find the right automation tool. Regardless of the implementation type, the tool must continue supporting the business's strategic decisions and innovations. ACCELQ, a Low-code/no-code test automation tool, draws a distinction from other tools by seamlessly supporting applications in all ways of implementation- on-premise, Cloud, Hybrid cloud, External solution integration, etc.

Sowmya Sridharamurthy
Sowmya Sridharamurthy is a seasoned product quality leader working as SDET Manager at Lytho. With 14+ years of experience handling products from inception to delivery, she has worked on diverse solutions- ERP, SAAS, Mobile Apps, and Web applications. She has a proven track record of successfully implementing result-driven test processes, non-disruptive migrations, and upgrades. Sowmya is driven to mentor development teams in building effective strategies and implementations to achieve ROI through test automation. Being an Accessibility advocate, she is keen on driving inclusive software development. Sowmya is an active community builder and runs an “APIans” meet-up group from Amsterdam."
Related Posts
 How to Build CI/CD for Microservices
How to Build CI/CD for Microservices
How to Build CI/CD for Microservices
 Top Salesforce Events to Attend in 2025
Top Salesforce Events to Attend in 2025

































