Understanding and Resolving Common Test Bugs in Software Testing

A software bug is a defect or error within an application that produces incorrect or unexpected results or causes the software to perform in unintended ways. Identifying and resolving these issues are important to maintain software stability and to provide an uninterrupted user experience. Bugs can be small hiccups or catastrophic errors that grind operations to a halt.
Data helps you find anomalies in software testing, which they can use to guide you in resolving them. Awareness of these and improving them help testers and developers in improving the quality of applications and usability.
8 Test Bugs That Can Break Your App (And How to Fix Them)
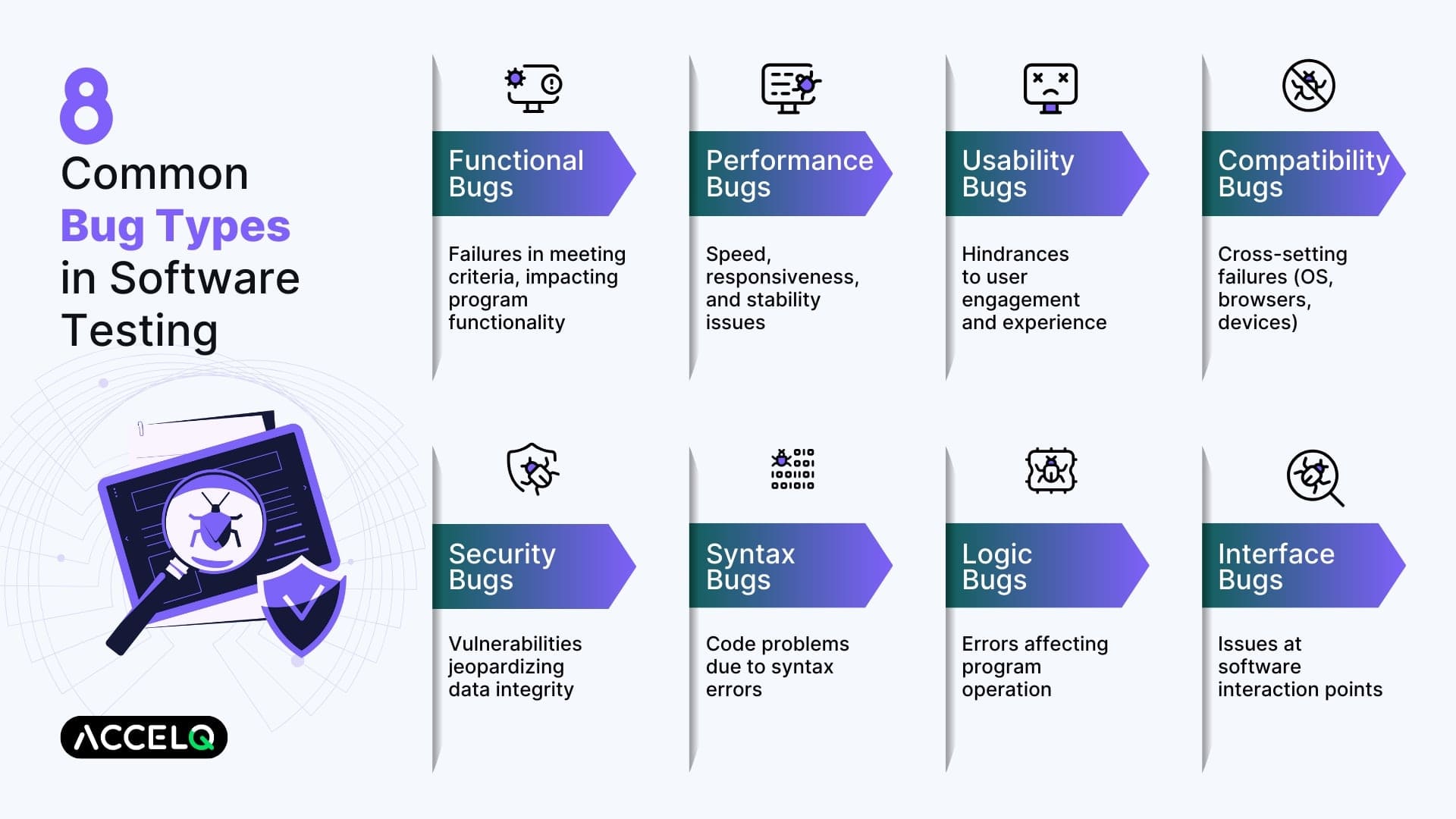
1. Functional Defects: The Backbone of Bug Detection
Functional bugs are among the most common and impactful software issues. These occur when a feature does not meet the intended requirements, causing disruptions in the application's core functionality.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Incorrect logic, missed requirements, or integration errors. |
| Impact | Directly affects usability, reliability, and user satisfaction. |
| Testing Approach | Verify each feature against the requirements to ensure functionality aligns with expectations. |
- An automated test case in ACCELQ is designed to validate the login functionality of a web application. The test fails due to incorrect validation logic, preventing valid users from logging in.
Pro Tip: Employ test-driven development (TDD) practices to catch functional test bugs early in the development cycle.
2. Performance Issues: Optimizing Speed and Responsiveness
Performance bugs impact an application’s speed, stability, and scalability. Left unchecked, these issues can degrade user experience and lead to application downtime.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Inefficient code, poor database queries, and lack of resource optimization. |
| Impact | Reduced application reliability and frustrated users. |
| Testing Approach | Conduct performance testing to measure speed, scalability, and resource usage. Optimize code and queries for efficiency. |
- An automated performance test in ACCELQ reveals that a critical transaction in a web application takes 5 seconds instead of the expected 2 seconds, highlighting the need for optimization.
Pro Tip: Use tools like JMeter or ACCELQ’s AI-driven performance testing features to simulate high loads and identify bottlenecks.
3. Usability Errors: Ensuring Seamless User Interaction
Usability bugs hinder a user’s ability to interact effectively with an application. While these types of computer bugs may not cause outright failures, they significantly affect user satisfaction and adoption rates.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Poor design choices, inadequate UI elements, and unintuitive workflows. |
| Impact | Frustrated users and reduced application engagement. |
| Testing Approach | Conduct usability testing and iterate designs based on user feedback. |
- A navigation bar button in a web application requires multiple clicks to respond, frustrating users and increasing task completion time.
Pro Tip: Conduct A/B testing to gather user feedback on UI changes and optimize usability.
4. Compatibility Failures: Bridging Cross-Platform Gaps
Compatibility bugs occur when software fails to perform uniformly across different environments, including browsers, operating systems, or devices. These issues lead to fragmented user experiences.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Differences in rendering engines, device hardware, and operating systems. |
| Impact | Limited accessibility and potential loss of users. |
| Testing Approach | Test the application across multiple platforms and devices to ensure consistency. |
- An automated compatibility test identifies that the file upload feature in a web application works in Chrome but fails in Safari, breaking workflows for a subset of users.
Pro Tip: Use cloud-based testing tools to streamline cross-platform testing.
5. Security Vulnerabilities: Safeguarding Data Integrity
Security bugs are critical vulnerabilities that allow unauthorized access, data breaches, or malicious attacks against software. Addressing these types of computer bugs ensures application integrity and user trust.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Improper input validation, insecure coding practices, and lack of encryption. |
| Impact | Data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. |
| Testing Approach | Perform security testing and implement secure coding standards. Regularly update and patch vulnerabilities. |
- An ACCELQ test finds an SQL injection vulnerability in a web application’s login form that could allow an attacker to manipulate the database.
Pro Tip: Include security testing in your CI/CD pipeline to detect vulnerabilities earlier.
6. Syntax Errors: Ensuring Code Accuracy
Syntax bugs occur when programming language rules are misapplied, leading to compilation or runtime errors. These test bugs are often easy to detect but can halt development if overlooked.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Typos, missing semicolons, or incorrect syntax usage. |
| Impact | Prevents the application from running, disrupting workflows. |
| Testing Approach | Use static code analysis tools and conduct thorough code reviews. |
- A missing semicolon in a JavaScript function prevents a critical script from running, disrupting application functionality.
Pro Tip: Automate syntax checks using linters and integrate them into your development environment.
7. Logical Errors: Correcting Flawed Algorithms
Logical bugs result from incorrect algorithms or flawed decision-making processes within the code. These issues produce inaccurate results and hinder application functionality.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Misunderstood requirements or flawed algorithms. |
| Impact | Leads to inaccurate application outcomes and user dissatisfaction. |
| Testing Approach | Validate algorithms using automated tests and peer reviews. |
- An e-commerce application calculates incorrect discounts due to flawed logic, affecting pricing accuracy.
Pro Tip: Break down complex algorithms into smaller units and test them individually to isolate issues.
8. Interface Discrepancies: Smoothing System Interactions
Interface bugs arise when different software components fail to interact seamlessly. These issues can cause data mismatches and disrupt system operations.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Sources | Miscommunications, mismatched data formats, or improper API handling. |
| Impact | Disrupts workflows and data integrity. |
| Testing Approach | Conduct comprehensive interface testing to ensure proper data exchange between components. |
- A backend API returns data in an unexpected format, causing a web application to display incorrect information.
Pro Tip: Use contract testing tools like Pact to verify API interactions and ensure compatibility.
Conclusion
This is where effective bug management comes into play. And how each bug type, from functional defects to security bugs, demands specialized tools and processes for detection and resolution to minimize disruption and maximize reliability. Tools such as ACCELQ have automated bug detection and resolution, making sure the development teams work to make their applications robust and user-friendly. Leverage ACCELQ’s AI-powered platform to address diverse bug types efficiently and elevate your software testing strategy.
Ready to transform your testing approach? Get a demo of ACCELQ today and explore how it can help you easily deliver defect-free software.
Prashanth Punnam
Sr. Technical Content Writer
With over 8 years of experience transforming complex technical concepts into engaging and accessible content. Skilled in creating high-impact articles, user manuals, whitepapers, and case studies, he builds brand authority and captivates diverse audiences while ensuring technical accuracy and clarity.
Discover More
 Test-Driven Development (TDD): A Comprehensive Guide
Test-Driven Development (TDD): A Comprehensive Guide
Test-Driven Development (TDD): A Comprehensive Guide
 Testing in Microservices Architecture with ACCELQ
Testing in Microservices Architecture with ACCELQ